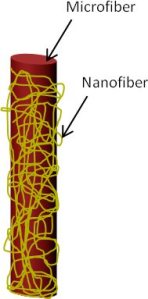
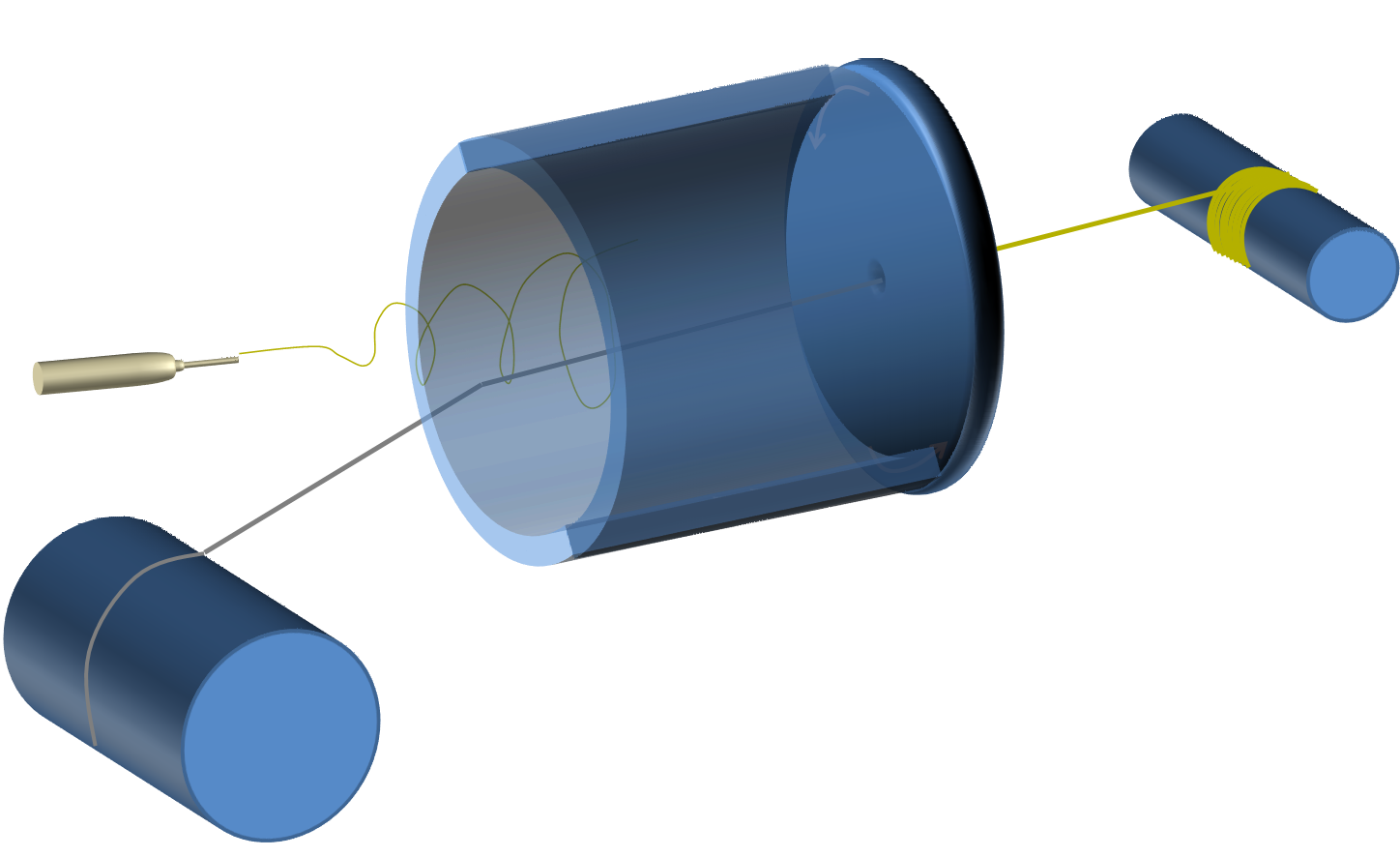
▼ Reference
- Shim I K, Suh W H, Lee S Y, Lee S H, Heo S J, Lee M C and Lee S J (2009) Chitosan nano-/microfibrous double-layered membrane with rolled-up three-dimensional structures for chondrocyte cultivation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 90A 595-602
- Edwards S L, Church J S, Werkmeister J A, Ramshaw J A M (2009) Tubular micro-scale multiwalled carbon nanotube-based scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30 pp. 1725
- Erben J, Pilarova K, Sanetrnik F, Chvojka J, Jencova V, Blazkova L, Havlicek J, Novak O, Mikes P, Prosecka E, Lukas D, Kostakova E. 3D micro-nano fibrous scaffold prepared by meltblown in combination with electrospinning for the bone tissue engineering. Nanocon 2014. Nov 5-7, Czech Republic. Open Access
- Erben J, Jirkovec R, Kalous T, Klicova M, Chvojka J. The Combination of Hydrogels with 3D Fibrous Scaffolds Based on Electrospinning and Meltblown Technology. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(11):660. Open Access
- Pham Q P, Sharma U and Mikos A G (2006) Electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microfiber and multilayer nanofiber/microfiber scaffolds: characterization of scaffolds and measurement of cellular infiltration Biomacromolecules 7 2796
- Thorvaldsson A, Stenhamre H, Gatenholm P and Walkenstrom P (2008) Electrospinning of Highly Porous Scaffolds for Cartilage Regeneration. Biomacromolecules 9 1044-1049 [126] Ekaputra A K, Prestwich G D, Cool S M and Hutmacher D W 2008 Biomacromolecules 9 2097
- Tuzlakoglu K, Santos M I, Neves N, Reis R L. Design of Nano- and Microfiber Combined Scaffolds by Electrospinning of Collagen onto Starch-Based Fiber Meshes: A Man-Made Equivalent of Natural Extracellular Matrix. Tissue Engineering Part A 2011; 17: 463.
▼ Credit and Acknowledgement
Author
Wee-Eong TEO View profile
Email: weeeong@yahoo.com
 ElectrospinTech
ElectrospinTech